Tuesday, January 29, 2008
Thursday, December 20, 2007
A variety of plants
Bryophytes (mosses and liverworts):
*No roots, vascular system, or cuticle.
*Rhizoids similar to root hairs.
*Mosses with simple leaf-like structures.
*Liverworts have flattened shape called a thallus.
*Roots, leaves in fronds, and vascular system.
*Cuticle on leaves.
*Can form small trees but not woody.
*Shrubs to very large trees.
*Advanced vascular system.
*Woody stems and roots.
*Advanced vascular system
*Roots, stems, and leaves
*Can form woody tissue
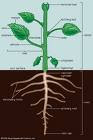 3) Draw a plant diagram to show the distribution of tissues in the stem, root, and leaf of a generalized dicotyledonous plant.
3) Draw a plant diagram to show the distribution of tissues in the stem, root, and leaf of a generalized dicotyledonous plant.
4) Explain the relationship between the distribution of tissues in the leaf and the functions of these tissues.
* Xylem : brings water to replace losses due to transpiration
* Phleom : transports products of photosynthesis. * Stoma : allows CO2 to diffuse in and O2 to diffuse out in reference to photosynthesis * Guard Cells : pair of cells which can open or close the stoma and control transpiration
5) Outline four adaptions of xerophytes
* Thick Stems : high amount of water storage * Vertical Stems : absorbs light * Wide Branching : absorbs water close to the surface
* Thick wax cuticle
6) Outline 2 structural adaptions of hydrophytes
* Air spaces in leaves cause buoyancy * Small amounts of xylem in stem and leaf


